This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
- Table of Contents
ELISA protocols and Troubleshooting guide for high quality and reliable data.
Browse Boster Featured ProductsELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. In ELISA, an antigen must be immobilized to a solid surface and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to an enzyme. Detection is accomplished by assessing the conjugated enzyme activity via incubation with a substrate to produce a measurable product. The most crucial element of the detection strategy is a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction.
ELISAs are typically performed in 96-well (or 384-well) polystyrene plates, which will passively bind antibodies and proteins. The binding and immobilization of reagents makes ELISAs simple to design and perform. Having the reactants of the ELISA immobilized to the microplate surface enables easy separation of bound from non-bound material during the assay. This ability to wash away non-specifically bound materials makes the ELISA a powerful tool for measuring specific analytes within a crude preparation.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) principles are very similar to other immunoassay technologies. ELISAs rely on specific antibodies to bind the target antigen, and a detection system to indicate the presence and quantity of antigen binding. In order to maximize the sensitivity and precision of the assay, the plate must be carefully coated with high-affinity antibodies – a process that Boster Bio has mastered.
Did you know that Boster, the leading ELISA manufacturers are providing research-grade CRO services? Outsource your ELISA experiments today and save your time and money.
Our 2300+ ELISA kits are validated in multiple sample matrices from serum and saliva to urine and feces, ensuring wide application ranges for you to select from. Boster's mission is to support research in areas such as immunology, neuroscience, cancer, and more by providing the high-quality ELISA kits needed to get better results. Here are the list of our most popular ELISA kit.
Comparisons on Direct, Indirect, Sandwich, Competitive ELISA
ELISAs can be performed with a number of modifications to the basic procedure: direct, indirect, sandwich or competitive. The key step, immobilization of the antigen of interest, can be accomplished by direct adsorption to the assay plate or indirectly via a capture antibody that has been attached to the plate. The antigen is then detected either directly (enzyme-labeled primary antibody) or indirectly (enzyme-labeled secondary antibody). The detection antibodies are usually labeled with alkaline phosphatase (AP) or horseradish peroxidase (HRP). A large selection of substrates is available for performing the ELISA with an HRP or AP conjugate. The choice of substrate depends upon the required assay sensitivity and the instrumentation available for signal-detection (spectrophotometer, fluorometer or luminometer).
Among the standard assay formats discussed and illustrated below, where differences in both cpture and detection were the concern, it is important to differentiate between the particular strategies that exist specifically for the detection step. However an antigen is captured to the plate (by direct adsorption to the surface or through a pre-coated "capture" antibody, as in a sandwich ELISA), it is the detection step (as either direct or indirect detection) that largely determines the sensitivity of an ELISA.
General ELISA Workflow, a step-by-step ELISA protocol
96-Well Plate Pre-Coated with Capture Antibody (Choose from Boster's ELISA Kit)
| STEPS | INDIRECT | DIRECT | SANDWICH | COMPETITIVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capture Ab Coating | ||||
| Antigen Coating | ||||
| Blocking | ||||
| Sample (Antigen) Incubation | ||||
| Primary Ab Incubation | ||||
| Secondary Ab Incubation | ||||
| Substrate Prep | ||||
| Signal Detection | ||||
| Data Analysis |
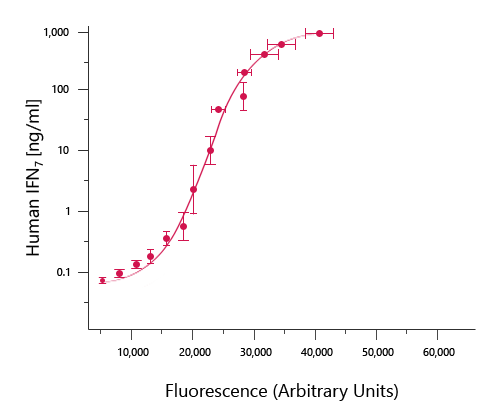
ELISA data is typically graphed with optical density (or fluorescence) vs concentration to produce a sigmoidal curve as shown above.
This guide will teach you everything you need to become an ELISA expert, including a critical review of principles, all-in-one FAQs, and more.
Picokine ELISA kits are Boster Bio manufactured ELISA kits that have Picokine level sensitivity. Our ELISA kits come with over 20 years of manufacturing expertise and proprietary methods which provide the precision you need.
Boster Bio is proud to offer over 1,000 ELISA kits for a wide range of targets. With over 20 years of experience in antibody and ELISA kit manufacturing, Boster Picokine™ enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits are guaranteed to be sensitive, specific, and stable. We rigorously validate every lot against a wide range of samples to ensure consistent, reliable results. Join over 14,000 scientists who put their trust in Boster Picokine™ ELISA kits.
Boster's Picokine™ ELISA kits are made with high affinity antibodies that can detect native form proteins with picogram and subpicogram level sensitivity.
Boster's QC department validates our ELISA kits against proteins in relevant superfamilies and proteins with similar immunogenicities to ensure specificity to the analytes of interests.
Our 2300+ ELISA kits are validated in multiple sample matrices from serum and saliva to urine and feces, ensuring wide application ranges for you to select from.
Boster has been serving the research community since 1993 and cited by 23,000+ publications. Our team of experts are dedicated to provide you the best customer service.
Cited by more than 1000+ publications
Don't see what you want? Ask us at [email protected]
Here are the 212 most popular ELISA kits.
![]()
ELISAs can accurately assess soluble proteins in their native state, so they are ideal for samples such as urine or saliva. Check out the ELISA sample preparation guides to learn how to get the best results from your sample type.
Learn our ELISA Sample Preparation![]()
Learn stepwise ELISA protocols from reagent preparation to data analysis. Check out their differences to learn how they compare and their advantages and disadvantage.
Learn our ELISA protocol![]()
Get to know some ELISA troubleshooting tips with this Guide. It has some commonly encountered problems and solutions to ELISA.
Check our ELISA troubleshooting tips![]()
Learn how to perform ELISA data analysis. Get to know the different aspects to consider for more consistent and accurate ELISA data. Furthermore, we provide a step-by-step guide to create a standard curve for analysis.
Browse ELISA Data analysis